Ocean Water Color By Depth
Light and Colour in the Deep Sea
What happens to calorie-free as information technology travels downwardly through the depths of the ocean? How does it affect the colors we see?
What is Light
Light is energy traveling at the fastest speed in the universe through what are called low-cal waves. Dissimilar body of water waves, light waves are electromagnetic free energy. Like all electromagnetic energy, they accept different wavelengths.
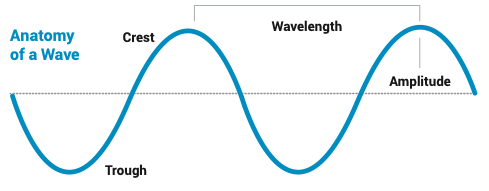
Parts of a wave:
- Crest– the highest point of a wave
- Trough– the lowest bespeak of a moving ridge
- Wavelength– the altitude betwixt two waves
- Amplitude– the meridian or depth of a moving ridge; one/ii the length of the vibration path
- Frequency– the number of waves that laissez passer a fixed betoken in a period of fourth dimension

Lite Under Bounding main Waves
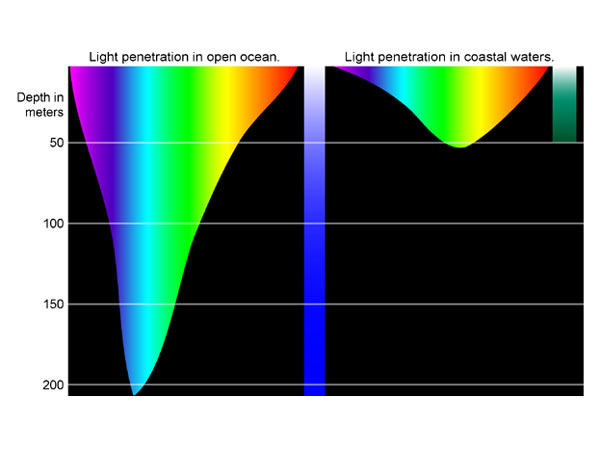
Sunlight contains all of the colors of our visible spectrum— red, orange, xanthous, light-green, blueish, and violet (ROYGBV). When all of these colors are combined together, they appear white as white light. Each visible color has its own wavelength, or altitude betwixt two waves. Scarlet light has the longest wavelength in the visible spectrum and violet has the shortest wavelength. Wavelength shortens every bit you move in sequence from cherry to violet light across the spectrum.
Wavelength is likewise related to energy. Colors with shorter wavelengths, like those on the blue and violet finish of the spectrum, have more energy than colors with longer wavelengths. Cherry light has the lowest free energy. In water, colors with lower energy, such as reds, oranges, and yellows are filtered out chop-chop. Because bluish and violet light waves have more than energy, they travel deeper through water.

Eyes in the Twilight Zone
Very little lite from the surface penetrates between 200 and 1,000 meters, in what's known every bit the dysphotic or twilight zone. One time nosotros reach about 1,000 meters depth, light from higher up has disappeared entirely. This sunless realm is known as the aphotic zone.
Light atmospheric condition affect how much both humans and organisms come across. Some deep- sea organisms' eyes have evolved to improve their vision in low light. They can be 10 to 100 times more sensitive to light than human optics. This is one of their astonishing adaptations that helps them survive. Meanwhile, some other abyssal animals have completely lost their ability to see. They rely on other senses, instead.

What Colors Are Establish in the Deep?
The wavelength of light that reflects off an object is the color we come across. For example, an object we run across as red in white light appears that mode because it reflects longer, less energetic ruby-red light waves. Information technology absorbs the other colors (all of which are present in white lite).
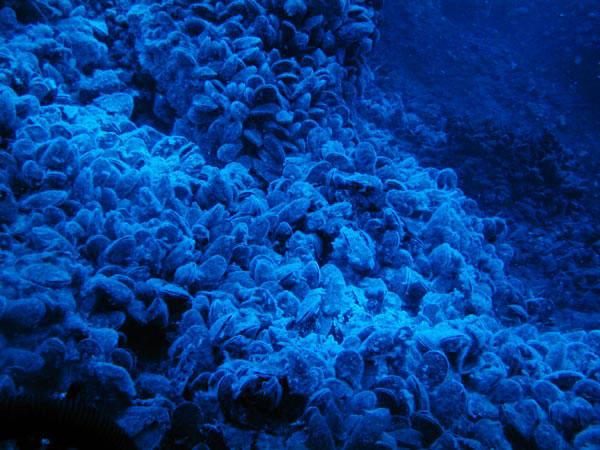
Red and orangish calorie-free waves accept less energy, so they are captivated nigh the ocean surface. Blue light penetrates much further, so blueish objects are more visible in the deep.
What Color of Animals Practise We Discover At that place?
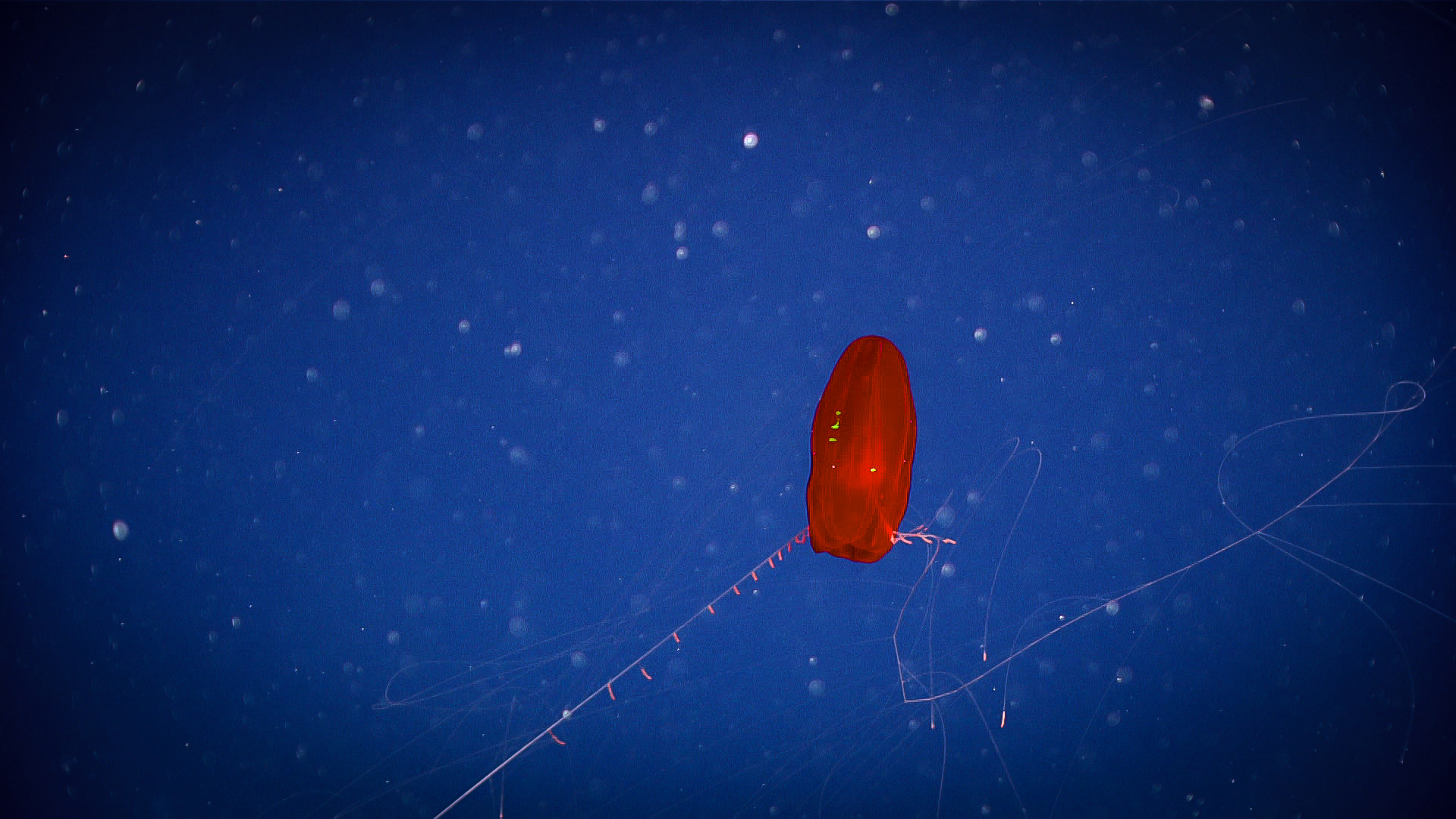
Scarlet and black animals are common in the deep ocean. At this depth, few, if any, blood-red calorie-free waves reverberate dorsum to one'southward eye. Since there is no scarlet lite available, red animals hither will announced grey or blackness, making them nearly invisible to other organisms. This helps them evade predators when at that place is nowhere to hide.

Additional Resources:
Why are and so many deep-sea animals ruddy in color?
How does depth impact the colour of marine animals?
Deep Light
Ocean Water Color By Depth,
Source: https://deepoceaneducation.org/resources/light-and-color-in-the-deep-sea/
Posted by: owenscrind1984.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Ocean Water Color By Depth"
Post a Comment